|
Metal surface treatment-shot peening process introduction
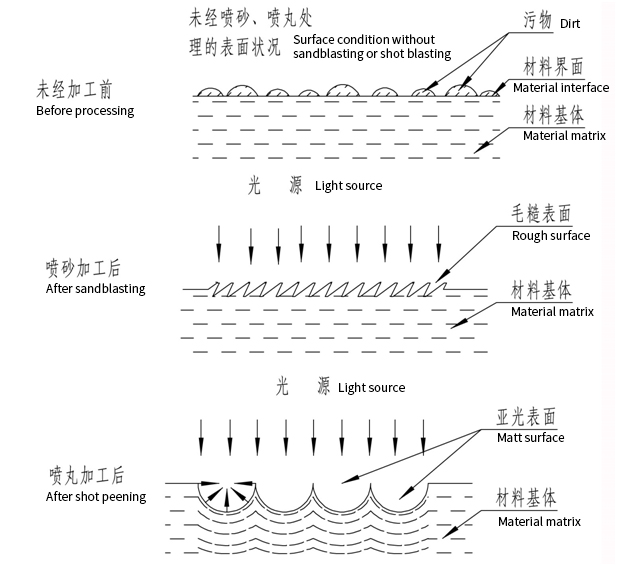
1. Shot peening Shot blasting uses a high-pressure fan or compressed air as power to eject a 0.2-2.5mm diameter projectile and impact the metal surface. Widely used in the extinction and descaling of metal surfaces; improve the mechanical strength, fatigue resistance, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of parts; eliminate the residual stress of casting, forging, and welding parts. Surface cleaning function Surface treatment with shot blasting has great impact force, obvious cleaning effect and high power consumption. Generally, shot blasting is used to eliminate oxide scale, rust, sand and old paint film on medium and large metal products and castings and forgings that are not less than 2-6mm in thickness or that do not require accurate dimensions and contours. Surface coating (plating) A method of cleaning up the previous paragraph. Principle: When the steel shot hits the surface of the workpiece (whether it is shot blasting or shot blasting), the metal substrate is deformed. Because Fe3O4 and Fe2O3 have no plasticity, they peel off after being broken, and the oil film deforms together with the substrate. , Shot peening cannot completely remove oil stains. 2. Shot peening function Principle: When a steel shot hits the surface of a metal part, it is like a miniature rod hammer hitting the surface, making small indentations or depressions. In order to form depressions, the metal surface layer must be stretched. Below the surface, the compressed grains try to restore the surface to its original shape, creating a hemisphere under high compressive force. Numerous depressions overlap to form a uniform residual stress layer. Finally, under the protection of the compressive stress layer, the fatigue strength of the parts is greatly improved. For example, the high-speed projectile is sprayed onto the spring surface to plastically deform the surface of the spring, forming a certain thickness of the strengthening layer, forming a higher residual stress in the strengthening layer, due to the existence of the spring surface compressive stress, when the spring is under load It can offset a part of the stress resistance, thereby improving the fatigue strength of the spring. Shot peening is divided into general shot peening and stress shot peening. In general processing, the steel plate is in a free state, and the surface of the steel plate is hit with high-speed steel shots to generate pre-compression stress on the surface to reduce the tensile stress on the surface of the steel plate during work. Stress shot peening is to pre-bend the steel plate under a certain force and then perform shot peening.
3. Types of shot used for shot peening: cast steel shot, cast iron shot, glass shot The hardness of cast steel shot is generally 40~50HRC. When processing hard metals, the hardness can be increased to 57~62HRC. Cast steel shot has good toughness and is widely used, and its service life is several times that of cast iron shot. The particle size of shot peening is generally 0.8-1.2mm. The higher the shot peening strength is, the larger the particle size is. 4. Surface cleaning quality ⑴、Sa1—manual brushing and cleaning level (or cleaning level) The technical standard of Sa1 level treatment: oil stains, grease, residual oxide scale, rust spots and residual paint should not be visible on the surface of the workpiece; a large number of uniform metal spots appear on the surface after treatment. ⑵, Sa2—commodity cleaning level (or industrial level) The technical standard of Sa2 level treatment: the surface of the workpiece should not be visible greasy, dirt, oxide scale, scale, paint, oxide, corrosive and other foreign substances (except for defects), but the defects are limited to no more than 33% of the surface per square meter , May include: slight shading; a small amount of slight discoloration caused by defects and rust; oxide skin and paint defects. If the original surface of the workpiece has dents, slight rust and paint will remain at the bottom of the dents. ⑶, Sa2.5—near-white clean-up level (or out-of-white level) Sa2.5 level is commonly used in the industry and can be used as the level of acceptance technical requirements and standards. The technical standard of Sa2.5 level treatment: the same as the first half of Sa2 requirements, but the defects are limited to no more than 5% of the surface per square meter, which can include: slight shadow; a small amount of slight discoloration caused by defects and rust; oxide scale and paint Defect. ⑷、Sa3—white cleaning level (or white level) Sa3 level is the highest processing level in the industry. The surface of the cleaned steel is completely silver-gray with a certain surface roughness to improve the adhesion of the layer. The technical standard of Sa3 level treatment: Same as Sa2.5 level, but 5% of shadows, defects, rust, etc. must not exist. The surface of the workpiece treated by shot peening is metallic, but because the surface is spherical, the light is partially refracted, and the workpiece will eventually become a matte effect (usually about 30 minutes). After shot peening, the surface of the workpiece is traced without damage, and the surface parts are increased. 5. Surface roughness ⑴The role of surface roughness: Increase the actual bonding area of the coating and the surface of the workpiece, and improve the bonding force of the coating The coating will produce a lot of internal stress during the curing process, and the presence of roughness can eliminate the stress concentration in the coating and prevent the coating from cracking The existence of surface roughness can support the weight of a part of the paint, which is beneficial to eliminate the sagging phenomenon, and the effect is especially obvious for the surface of vertical coating. ⑵Factors affecting roughness: Abrasive particle size, hardness, particle shape The hardness of the material of the work itself Pressure and stability of compressed air The distance and included angle between the nozzle and the surface of the workpiece ⑶Several problems related to surface roughness: The cleaning time has almost nothing to do with the surface roughness The angle between the nozzle and the surface will affect the surface roughness, but the change is not obvious between 45o and 90o Cleaning the surface with large abrasives can improve work efficiency, but it will increase the surface roughness. Studies have shown that abrasives with a particle size greater than 1.2mm cause higher roughness values. Re-cleaning the surface with high roughness with a small-grain abrasive can reduce the surface roughness to the specified value. The above is a brief introduction to the shot peening process, I hope it will be helpful to everyone.
|